The history
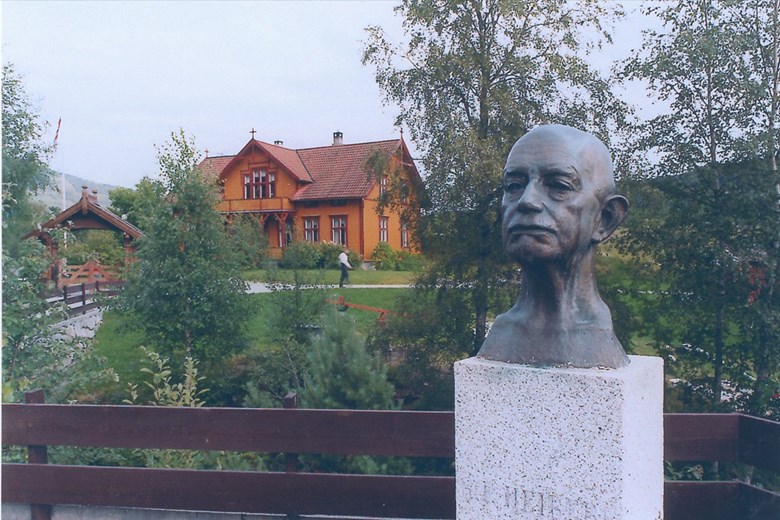
The museum was started with the collector activites of Gert Falch Heiberg, one of the major museum pioneers in Norway. Even as a young man he showed a keen interest in collecting. Around 1900, he started collecting objects and artefacts from everyday life and working life in Sogn. In 1903, Heiberg secured for himself the first antiquarian building, and in 1905, he built his first major exhibition hall. His ambitious idea of a "folkemuseum" (a people's museum) was now beginning to take shape. De Heibergske Samlinger - Sogn Folkemuseum was established in 1909, when Heiberg donated his private collection of antiques from Sogn to the newly established "Historielaget for Sogn" (The Historical Association for Sogn), which still owns the museum. The museum was developed on a separate section on Heiberg¿s property at Amla.

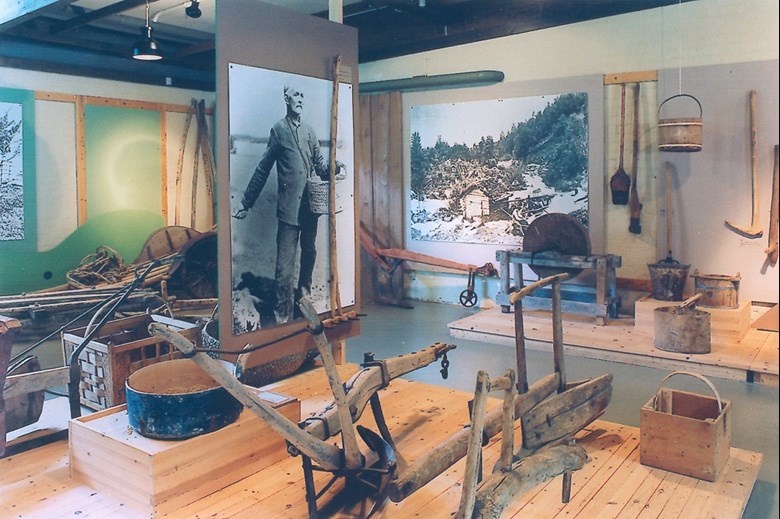
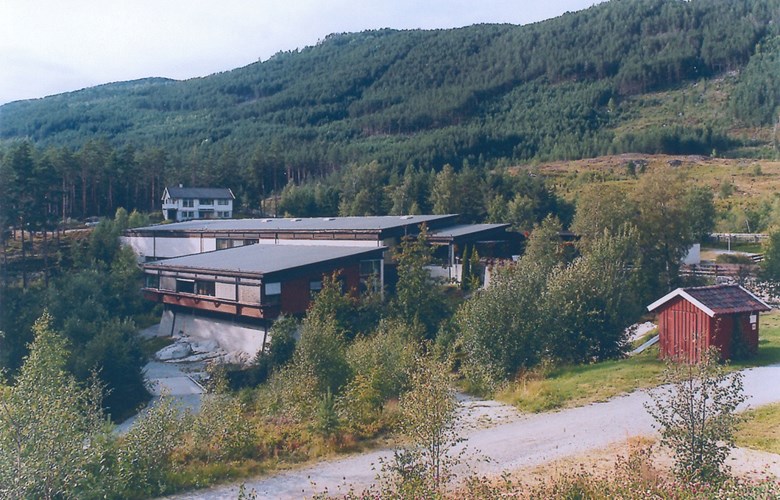
Gert Falch Heiberg developed the museum into becoming one of the foremost folk museums in the country. In addition to the many antiquarian buildings that were rebuilt on the museum premises, two big exhibition halls were built, and the museum obtained a status as the most comprehensive museum of farm implements in Norway. As early as in the 1950s, it became clear that the museum area at Amla was too small, and it was not suitable for a forward-looking development of the museum either. In the 1970s, then, the work of moving the museum to Kaupangerskogen, between Sogndal and Kaupanger was started. A new exhibition hall was taken into use in 1980, and today most of the buildings and objects and artefacts have been moved to the new museum. In addition to all the buildings, a new cultural landscape has been designed that is taken care of by means of traditional farming methods. In 1990, the Sogn Fjordmuseum was opened in a rebuilt saw mill close to the Kaupanger ferry quay.

Area of responsibility
At the start the museum had the whole area of Sogn as its area of responsibility. Now this has been reduced to only comprising the municipalities of Høyanger, Vik, Balestrand, Leikanger, Aurland, Sogndal, Lærdal, Årdal and Luster. The museum, however, has still a lot of objects from the western villages along the Sognefjord, and will continue its responsibility for these, both through its collection of objects and artefacts, as well as through the "Årbok for Sogn" (Yearbook for Sogn) published by Historielaget for Sogn.
The museum has traditionally covered a wide range of themes. It has been a ¿folk museum" which has attempted to cover all aspects of popular culture. Agriculture, hunting and fishing, all kinds of handicrafts, clothes and cloths, church life, building culture, and living environments, all these are themes that the museum has been especially interested in. The museum was among the first to go in for documentation of the present and the immediate past, and today the documentation of our immediate past is a major target area for De Heibergske Samlinger - Sogn Folkemuseum.
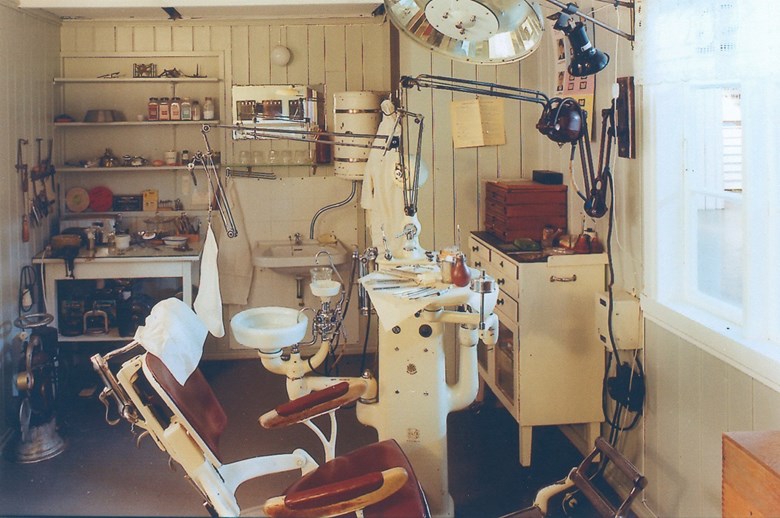
The collections
The museum also has a photo collection and owns much archive material. The archive material is stored at the County Archives of Sogn og Fjordane.
In addition to the museum premises at Kaupangerskogen, the museum owns Stedje mill, the private home Elvhaug, a smallholding at Eidet with a boat-building workshop, and a gate saw at Tingastad, all located within the municipality of Sogndal.
Further information on the museum can be found on the museum pages on "Kulturnett Sogn og Fjordane" and on the museum's own websites.